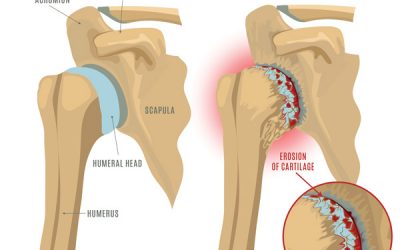
Shoulder labral tear tends to cause significant pain and inflammation as per the number of tissues being damage and compromised from the trauma. There is a crepitus (clicking) sound that develops once the labral structure is compromised. Morning stiffness and reduced joint overall movement are common symptoms reported by patients.
Shoulder labral tears and the associated corresponding misalignment
Bankart Tear is an injury at the inferior portion of the labrum and is predisposed by a chronic Anterior inferior (AI) shoulder misalignment resulting a direct irritation on the inferior portion of the labrum.
SLAP tear is an injury at the superior portion of the labrum where the long head of the biceps attached and is predisposed by a chronic externally rotated (AEX) inferior (AI) shoulder misalignments causing a traction injury of long head of the biceps to the superior portion of the labrum.
Is important to note that for the labrum to become injured, the previous defence mechanism have to have failed to allow the biomechanical stress to damage the ligamentous and labrum, therefore, the treatment care must aim to restore the health of the entire shoulder complex protective structures.
Assessment Protocol
The entire upper extremity biomechanical chain must be evaluated as per the neurological and mechanical influences of the spine, elbow, and hand.
Clinical assessment to identify the key dysfunctions of the shoulder complex that have contributed to this condition. Soft tissue analysis to pinpoint the level of irritation in the ligaments.
X-ray
Anterior – Posterior (AP) shoulder view is essential to analyse the level and direction of the different patterns of shoulder misalignments
MRI
Shoulder MRI is essential for visualizing the extent of injury on the muscle/tendon and ligamentous and labrum layers.
Locate the exact injury point; Allows the treatment to be more specific during the application of the treatment modalities
Identify the extent of tissue damage and the presence of scar tissue; Provides valuable information regarding prognosis and the application of friction soft tissue modalities to aid on scar tissue removal.
Treatment protocol
Specific shoulder adjustments followed by a rehabilitation regime to strengthen the entire soft tissue support of the shoulder .
Application of Low-level Laser and PEMF to aid on the cellular level of heling as well as improving the microcirculation for the area.
Friction soft tissue therapy helps to reduce dysfunctional scar tissue
Specific selected essential oil application to enhance healing
Depending on level of misalignment and chronicity a minimum of 6 weeks up to 12 weeks of treatment care may be necessary to resolve this deformity.